Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into spaceA greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gasesThis is called the "greenhouse effect"Most greenhouse gases are natural water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth Other greenhouse gases are carbon A carbon footprint is defined as the total amount of greenhouse gases produced to directly and indirectly support human activities, usually expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) In other words When you drive a car, the engine burns fuel which creates a certain amount of CO2, depending on its fuel consumption and the driving distance

Global Warming Key Words Combustion Carbon Dioxide Methane Deforestation Ppt Video Online Download
Greenhouse gases biology def
Greenhouse gases biology def-Lecture 1 covers seed biology, and the cultural requirements for germination and healthy seedling development Lecture 2 examines the rationale and associated costs and benefits of solar and conventional greenhouse structures, and the prevention/management of common greenhouse pest and pathogens The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of




The State Of The Global Climate World Meteorological Organization
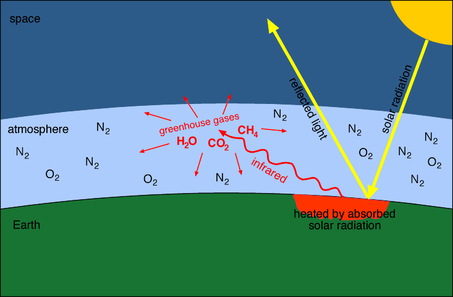
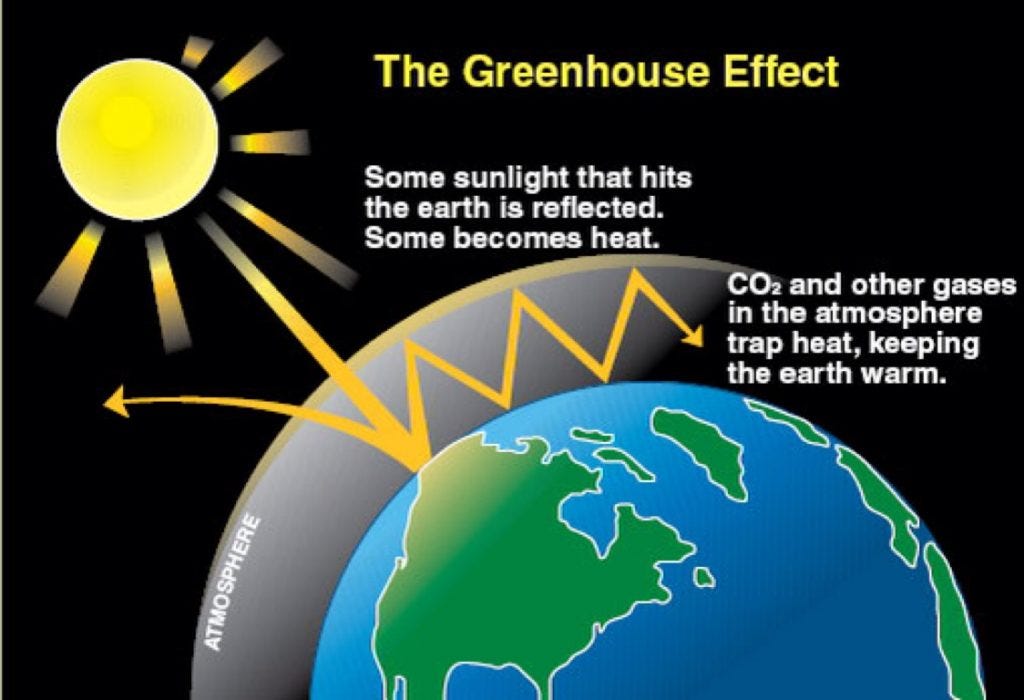
Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortableThe greenhouse effect occurs as the temperature within the Earth's atmosphere rises Greenhouse gases trap the heat within the Earth's atmosphere As sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, it passes through the gaseous layer and the Earth's surface absorbs part of the energy and reflects some energyGreenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth
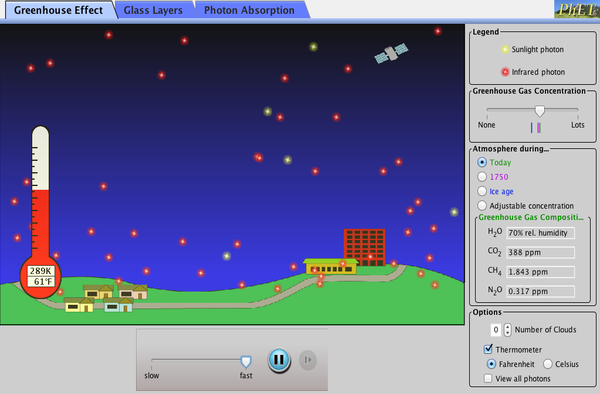
Greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide over the past 00 years Data are from ice core records and contemporary measurements4 Greenhouse gases occur naturally and allow us to survive on Earth by warming air near Earth's surfaceGreenhouse gases (https//wwwepagov/climateindicators/greenhousegases) are considered to be the most significant factor driving observed climate change in the past half a century Scientists Can Convert CO2 Into FuelGreenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by shortwave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longerwavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;
FACTFILE˜˚˛˝˜˙ˆˇ˘ GCSE fiflfi BIOLOGY GLOBAL WARMING˙ˆˇ˘ fifi fifi˜˚˛˝˙ˆˇ˛ˆ˘˚ˇ 2 the greenhouse effect by looking at the two planets closest to us, Mars and Venus Not enough greenhouse effect The planet Mars has a very thin atmosphere with not enough carbonWortformen (plural) greenhouse gases Substantiv ( Extractive engineering General) A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is widely considered CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we know it But there are many other gases (as well as substances like aerosol particles) that have roles in atmospheric warming and some of them have been emitted into our atmosphere largely as a result of human activity



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Global Temperatures Global Mean Temperatures As An Indicator Of Global Climate Change
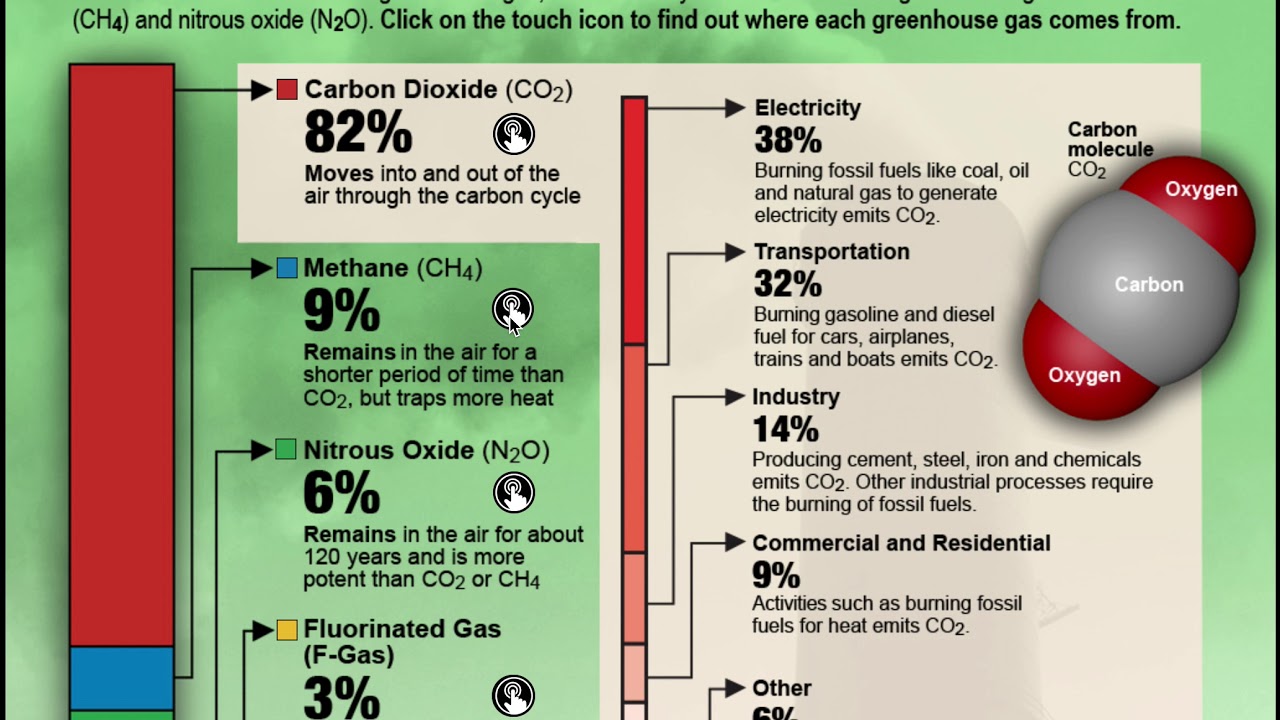
Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back toOverview of Greenhouse Gases Overview Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide Fluorinated Gases Total US Emissions in 19 = 6,558 Million Metric Tons of CO 2 equivalent (excludes land sector) Percentages may not add up to 100% due to independent roundingVarious farming activities produce carbon dioxide and methane gas These add to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and increase the temperature of the earth Overpopulation Increase in population means more people breathing This leads to an increase in the level of carbon dioxide, the primary gas causing global warming, in the atmosphere




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science



Greenhouse Gases Biology Notes For Igcse 14
Greenhouse gases produced by human activity are the most significant driver of climate change (Image credit ) Since the middle of the th century, greenhouse gases produced by DEFINITION OF GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is understood to result from an overall, longterm increase in the retention of the sun ' s heat around Earth due to blanketing by " greenhouse gases, " especially CO 2 and methaneThese "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it When we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




6 Humans Affect Climate
The greenhouse gases 5 procedure, which is very similar to the way a greenhouse works, is the main reason why the In fact, the greenhouse effect would collapse gases that can produce this outcome are were it not for the presence of carbon dioxide collectively called as greenhouse gasesThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Greenhouse gas definition Greenhouse gases are the gases which are responsible for causing the greenhouse effect Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human madeWater vapor and what expert scientists consider the four other 'most important' greenhouse gases comprise the veritable 'hit parade' of greenhouse gases that trap heat in Earth's atmosphere and contribute to overall warming across the globe There's a




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas The largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and RussiaOne of several gases, especially carbon dioxide, that prevent heat from the earth escaping into space, causing the greenhouse effect We need a global system for limiting greenhouse gasClimate change refers to significant changes in global temperature, precipitation, wind patterns and other measures of climate that occur over several decades or longer Discover an AZ glossary of concise scientific explanations to help readers better understand climate change from science to



Forests And Climate Change




Planktonic Algae Definition Glossary Details Oilgae Greenhouse Gases Glossary Biology Class
Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effect Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthDefine greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth



What Does Greenhouse Gases Mean Definition Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Stands For Carbon Dioxide And Other Gaseous Emissions Resulting From Human Activity That Cause Heat To Be Trapped In



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium
The greenhouse effect traps some of the energy from the Sun, which keeps our planet at a suitable temperature for life The problem is that ourGreenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn moreGreenhouse gases emitted by human activities alter Earth's energy balance and thus its climate Humans also affect climate by changing the nature of the land surfaces (for example by clearing forests for farming) and through the emission of pollutants that affect the amount and type of particles in the atmosphere



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Heat Phet Interactive Simulations




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
Thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Greenhouse gas, any gas capable of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gases
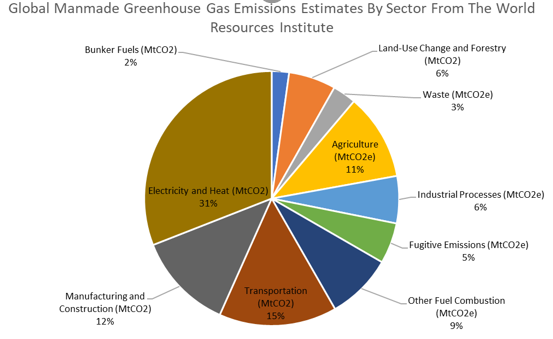



How Much Does Animal Agriculture And Eating Meat Contribute To Global Warming




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbons
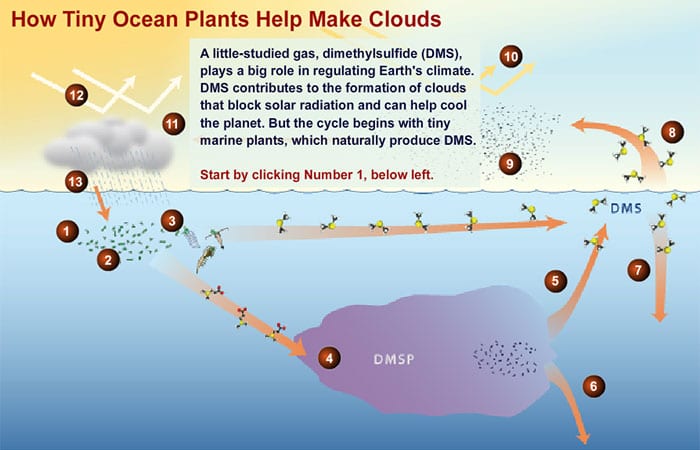



Dms The Climate Gas You Ve Never Heard Of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Ocean A Carbon Sink Ocean Climate Platform




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students



Air Pollution
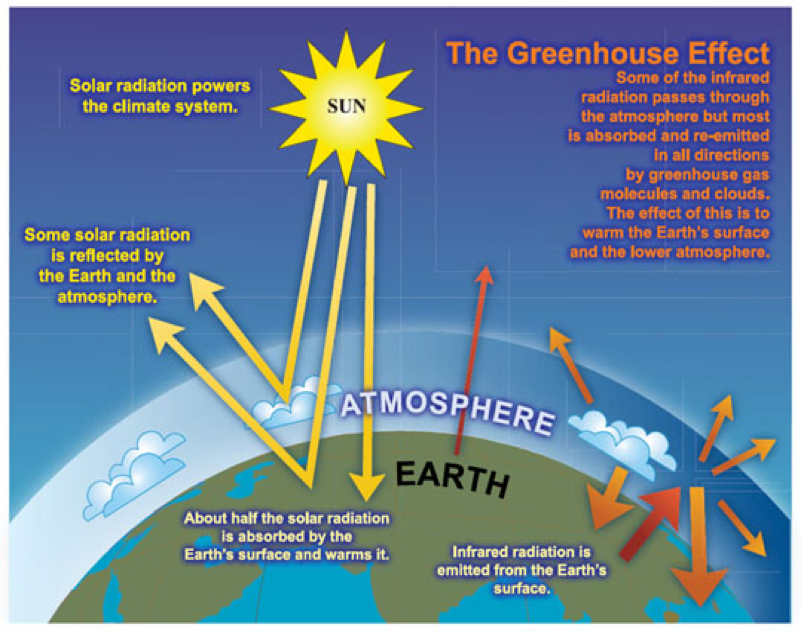



Greenhouse Gas Reduction
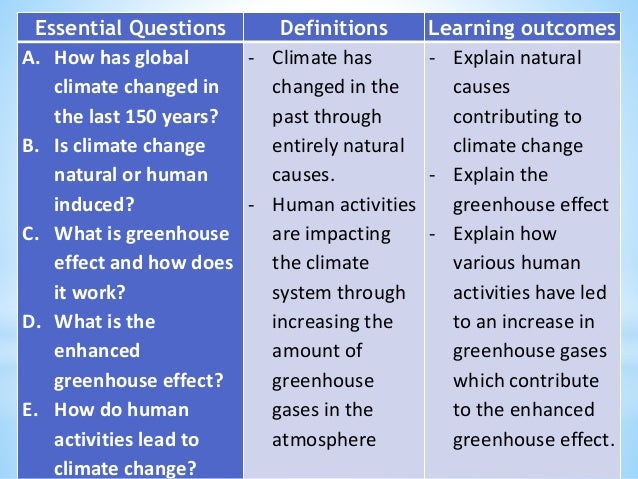



Greenhouse Effect Definition Biology Ib




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Global Warming Key Words Combustion Carbon Dioxide Methane Deforestation Ppt Video Online Download




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
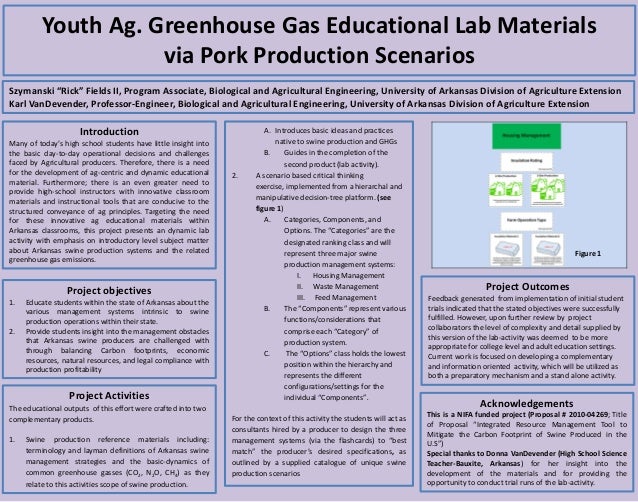



Youth Ag Greenhouse Gas Educational Lab Materials Via Pork Producti
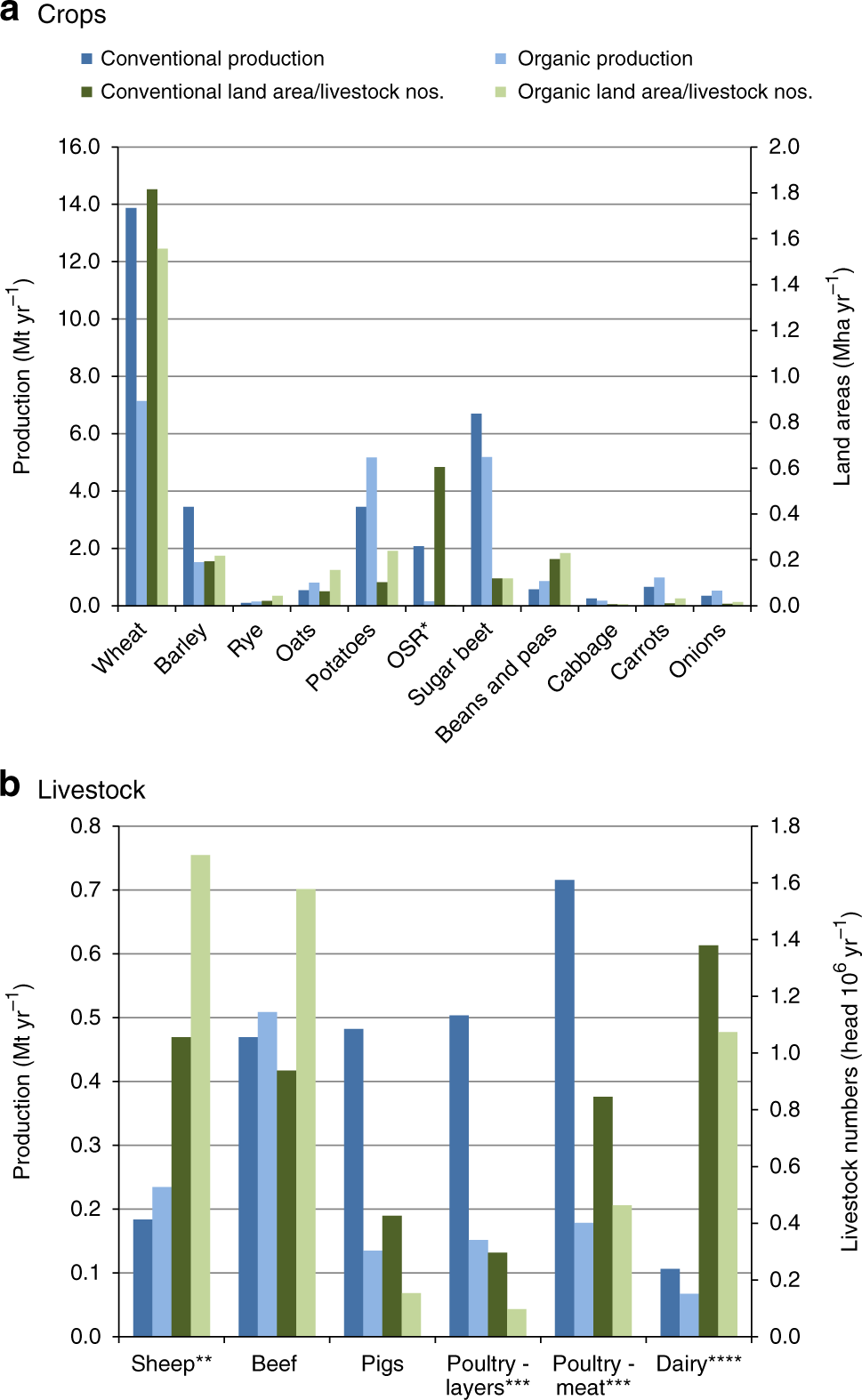



The Greenhouse Gas Impacts Of Converting Food Production In England And Wales To Organic Methods Nature Communications
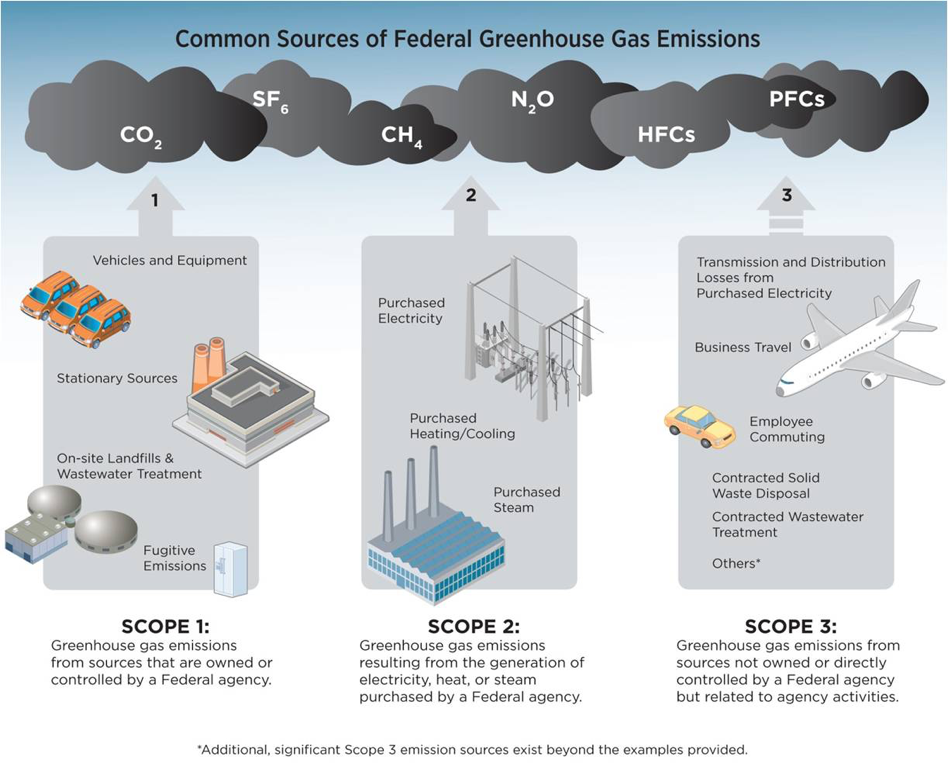



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
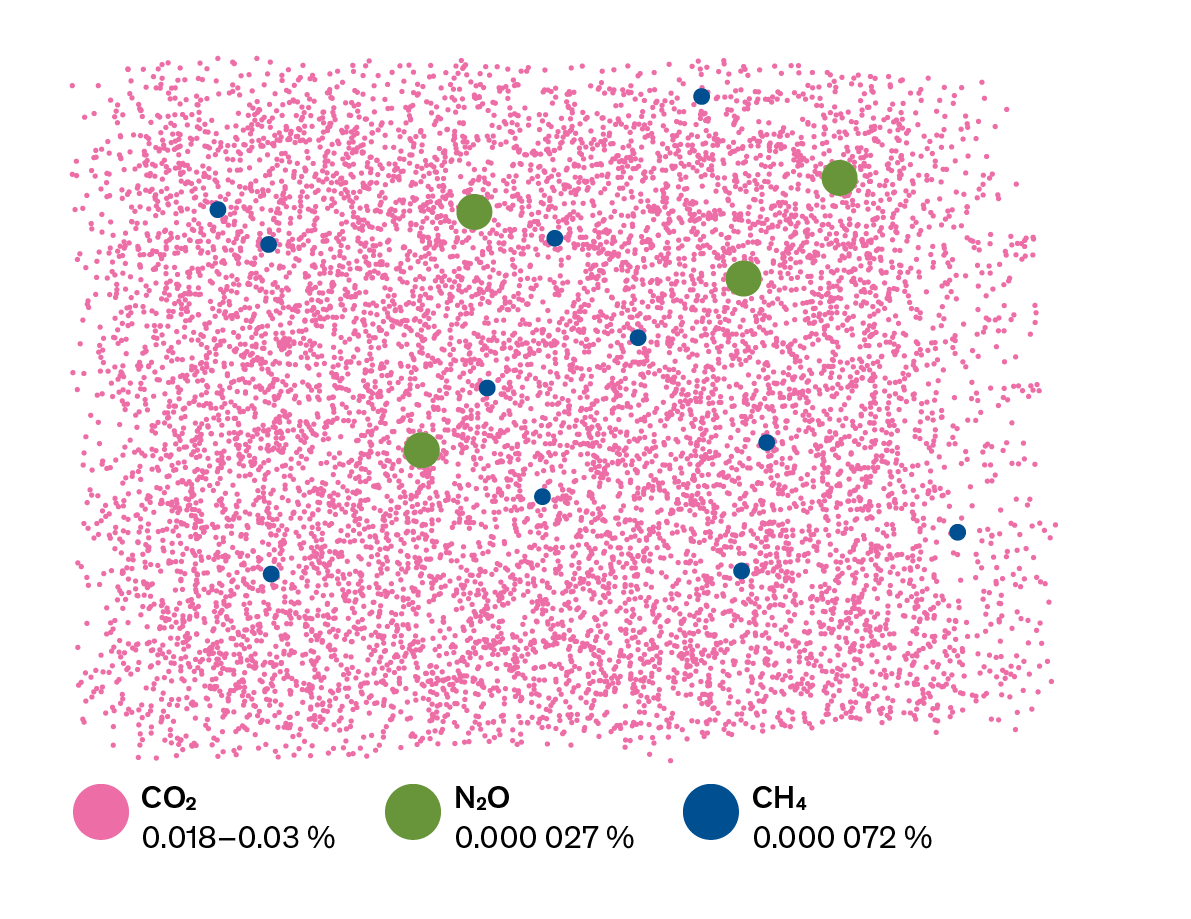



What Are Greenhouse Gases Myclimate




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
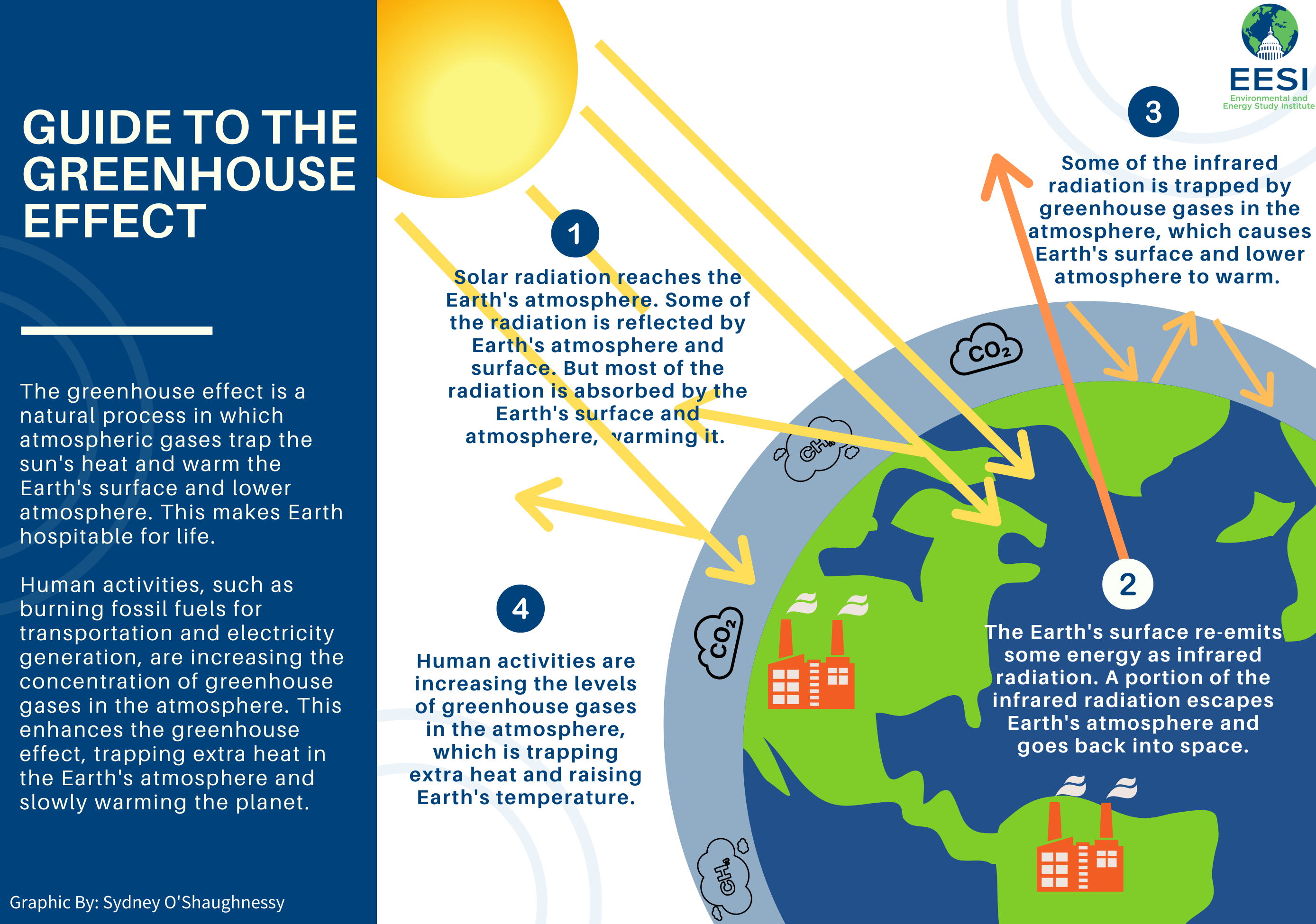



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Soils A Review Sciencedirect




Glossary Ipcc Task Force On National Greenhouse Gas Inventories




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases
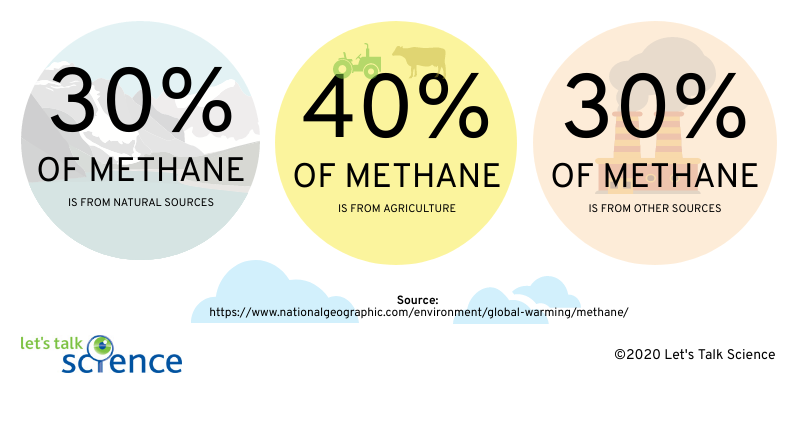



Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
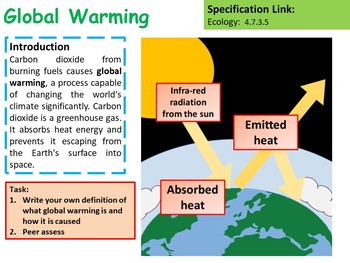



Biology Global Warming Lesson Activities By Mr Chalks Science Resources




The Greenhouse Effect And Our Planet National Geographic Society



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



2



Bimpactassessment Net Sites All Themes orp Impact Pdfs Em Calculating Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pdf




Livestock As Sources Of Greenhouse Gases And Its Significance To Climate Change Intechopen




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Biology Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion And Deforestation



Biology 150 Links On Greenhouse Effect Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Climate For Peace Toolkit By Sci Service Civil International Issuu




Biology Teachers Climate Guide




The Greenhouse Effect Edexcel Igcse Biology Revision Notes




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Cost Effective Implementation Of The Paris Agreement Using Flexible Greenhouse Gas Metrics Science Advances




Biology And Life Science Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




The State Of The Global Climate World Meteorological Organization




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




How To Use The Bio Grace Excel Greenhouse



1




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Topic 4 4 Climate Change Teacher Mrs Barnes Or Miss Andrea Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Earth System Modeling A Definition Climateurope



Greenhouse Effect Lincoln University



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




How To Use The Bio Grace Excel Greenhouse




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming



The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
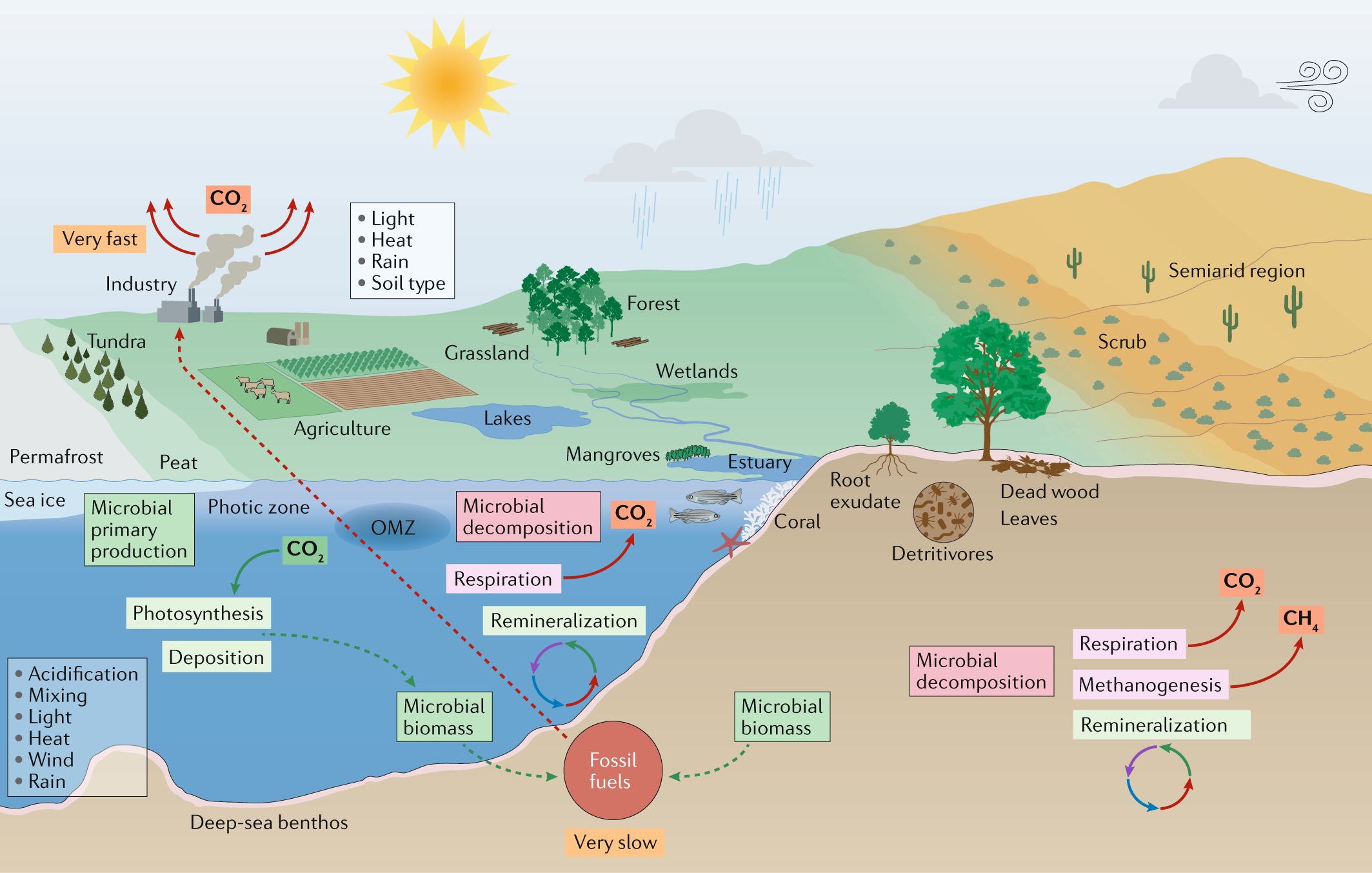



Scientists Warning To Humanity Microorganisms And Climate Change Nature Reviews Microbiology




Carbon Dioxide Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Definition Greenhouse Effect Define Greenhouse Effect Gases Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts
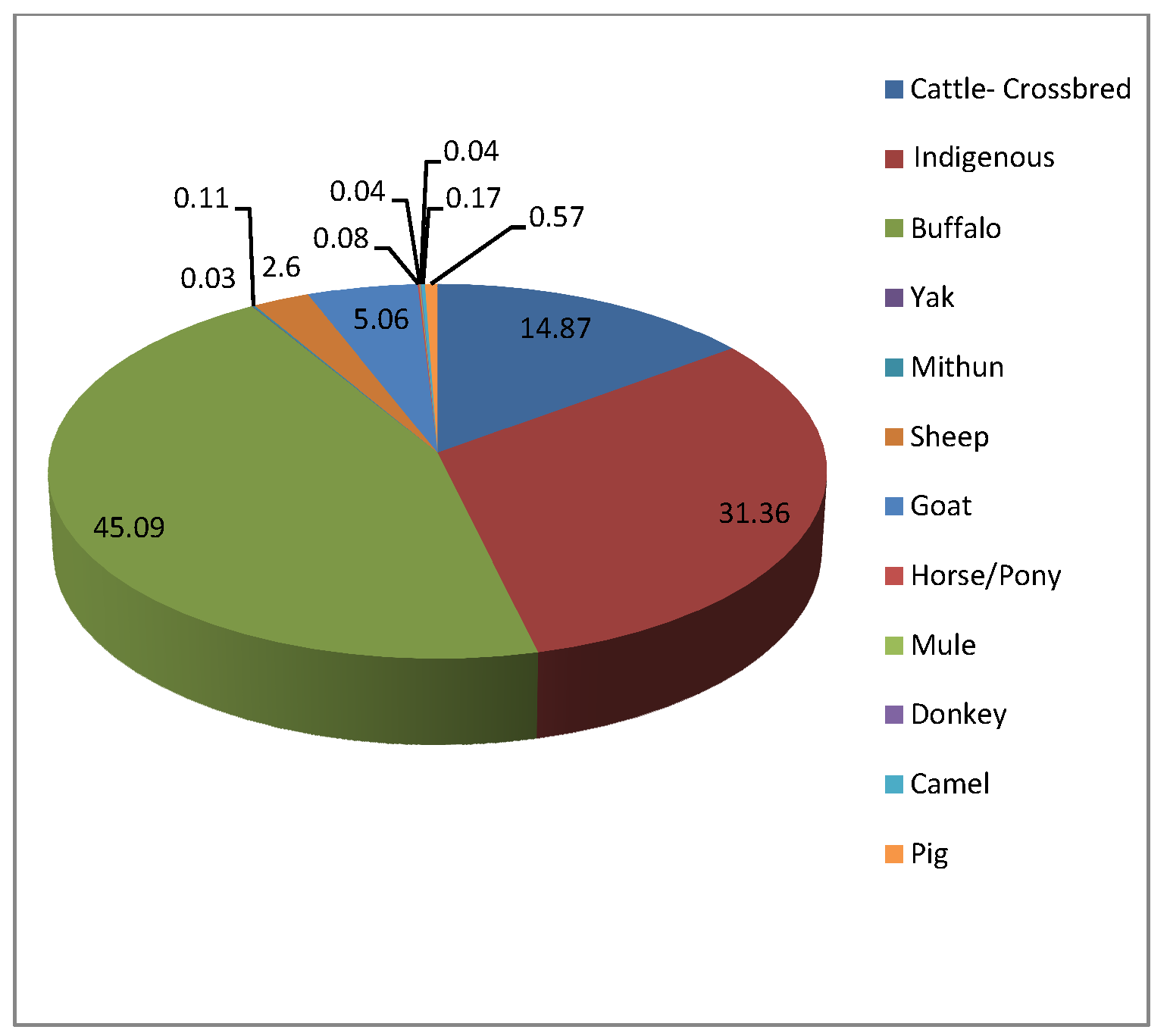



Livestock As Sources Of Greenhouse Gases And Its Significance To Climate Change Intechopen




Jrc Publications Repository Methane As Greenhouse Gas




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gases And Global Warming Ballotpedia




Appetite For Change



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



1



Biology 150 Links On Greenhouse Effect Global Warming




Definition Of Regenerative Agriculture How It Benefits Climate Change
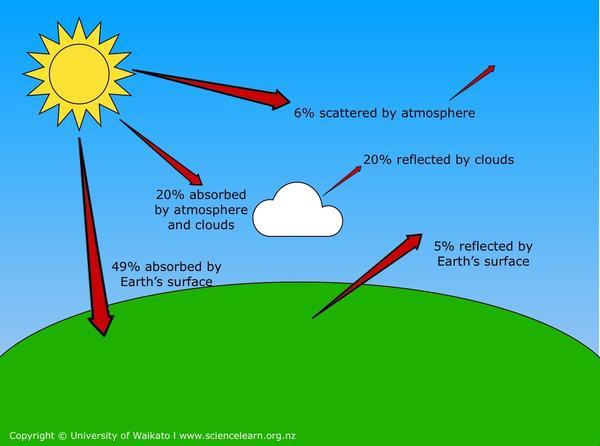



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿